Understanding Fertility: Fertility refers to the ability of an individual or a couple to conceive a child through natural means. It involves a complex interplay of factors, including the health of the reproductive organs, hormone levels, and overall well-being.
Common Causes of Fertility Issues:
1. Age: Female fertility declines with age, particularly after 35, due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs. Male fertility also decreases with age, although the decline is generally more gradual.
2. Ovulation Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation can result from conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hypothalamic dysfunction.
3. Tubal Issues: Blockages or damage to the fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from meeting the sperm, leading to infertility.
4. Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of it, leading to inflammation, scarring, and fertility problems.
5. Uterine Abnormalities: Anomalies in the structure of the uterus can affect implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage.
6. Male Factors: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and abnormal sperm shape can contribute to male infertility.
7. Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and drug use can negatively impact fertility for both men and women.
8. Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can affect fertility.
9. Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting ovulation and sperm production.
Treatments for Fertility Issues:
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising moderately, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, and managing stress can positively impact fertility.
2. Medications: Ovulation-inducing medications, such as Clomiphene citrate and Letrozole, can help regulate ovulation in women with ovulation disorders.
3. Surgery: Surgical procedures can address issues like blocked fallopian tubes, uterine abnormalities, and endometriosis.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): These advanced techniques include:
· Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is placed directly into the uterus during ovulation.
· In vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and then implanted into the uterus.
· Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to facilitate fertilization.
5. Donor Sperm or Eggs: When one partner has severe fertility issues, using donor sperm or eggs might be an option.
6. Gestational Surrogacy: If a woman can't carry a pregnancy, another woman (the surrogate) carries the pregnancy for her.
7. Adoption: when conceiving a biological child isn't possible, adoption offers an alternative path to parenthood.
Remember that fertility treatments vary based on individual circumstances, and consulting a medical professional or fertility specialist is essential to determine the most suitable approach for your situation.
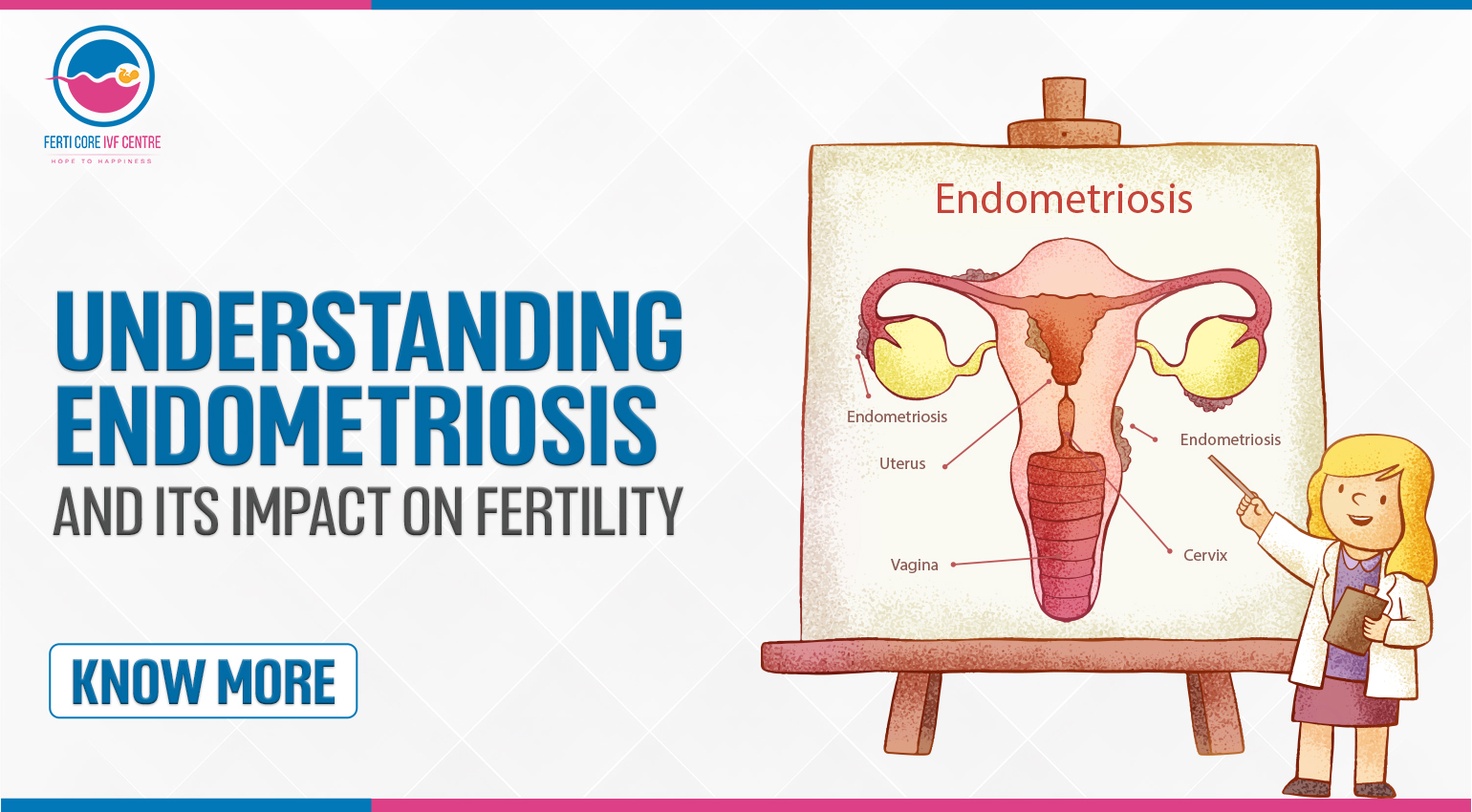 Understanding Endometriosis and its Impact on Fertility
Understanding Endometriosis and its Impact on Fertility
 10 Best Foods That Can Enhance IVF Success and Boost Fertility Naturally
10 Best Foods That Can Enhance IVF Success and Boost Fertility Naturally
 Navigating the IVF Journey: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the IVF Journey: A Step-by-Step Guide
 Personalized Care in IVF: Tailoring Treatments for Individual Needs
Personalized Care in IVF: Tailoring Treatments for Individual Needs
 Understanding Fertility: Common Causes and Treatments
Understanding Fertility: Common Causes and Treatments
 Things You Must Know About Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) Treatment- Ferticore IVF centre
Things You Must Know About Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) Treatment- Ferticore IVF centre
 Everything You Need To Know about Laparoscopy Surgery at Ferticore IVF Centre
Everything You Need To Know about Laparoscopy Surgery at Ferticore IVF Centre
 Unveiling the Path to Success with ICSI Treatment in Indirapuram - Ferticore IVF Centre
Unveiling the Path to Success with ICSI Treatment in Indirapuram - Ferticore IVF Centre
 10 Key Questions to Ask Your Fertility Specialist About IVF at Ferticore IVF Center
10 Key Questions to Ask Your Fertility Specialist About IVF at Ferticore IVF Center
 A Comprehensive Overview of Follicular Monitoring Procedure and Success Rates at Ferticore IVF Centre
A Comprehensive Overview of Follicular Monitoring Procedure and Success Rates at Ferticore IVF Centre
 Everything You Need to Know About Evaluation of Male Infertility
Everything You Need to Know About Evaluation of Male Infertility
 Understanding the Connection between Stress and Infertility
Understanding the Connection between Stress and Infertility
 7 Signs That Your Embryo Transfer May Have Been Successful
7 Signs That Your Embryo Transfer May Have Been Successful
 All You Need to Know About Preserving Female Fertility
All You Need to Know About Preserving Female Fertility
 Natural Strategies to Enhance Egg Quality for IVF Success - Ferticore IVF Centre
Natural Strategies to Enhance Egg Quality for IVF Success - Ferticore IVF Centre
Copyright © 2024 . Designed By Wafi Media Marketing Solutions Pvt. Ltd.